Our Activities
Crop Cultivation
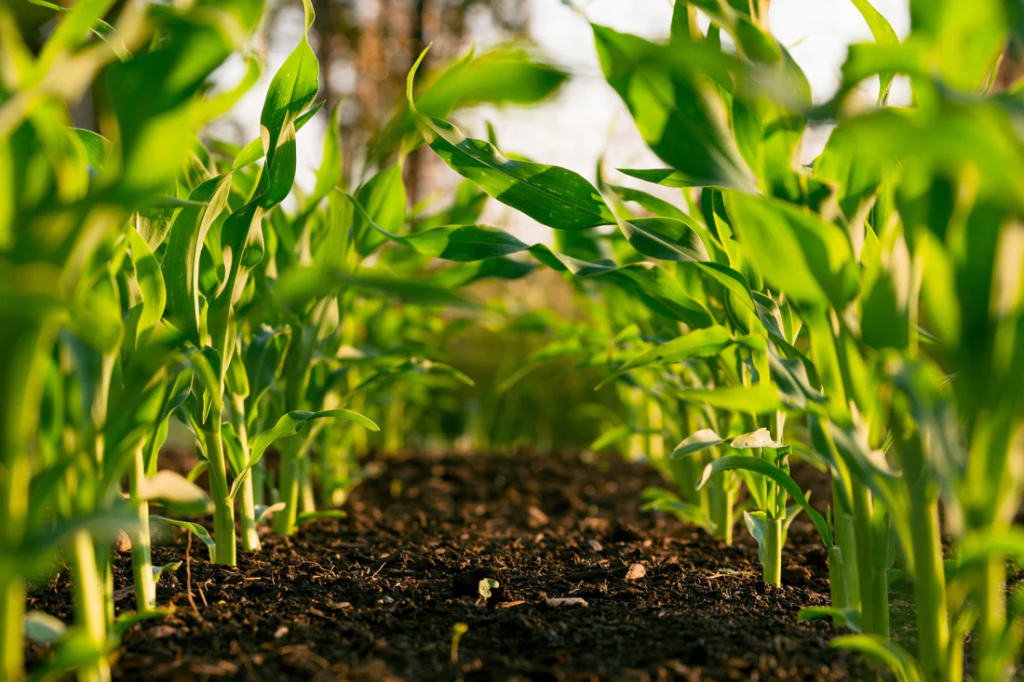

Crop cultivation in integrated farming involves growing different crops together or in rotation with other agricultural activities like livestock rearing or aquaculture. This approach maximizes land productivity, optimizes resource utilization, and enhances biodiversity on the farm. Integrated crop cultivation promotes natural pest and disease management through companion planting and crop diversity, reducing reliance on chemical inputs. It improves soil health by incorporating organic matter from crop residues and animal manure, leading to sustained fertility and structure. Overall, integrated crop cultivation fosters resilient and sustainable farming systems that benefit both farmers and the environment.
Live Stock Rearing
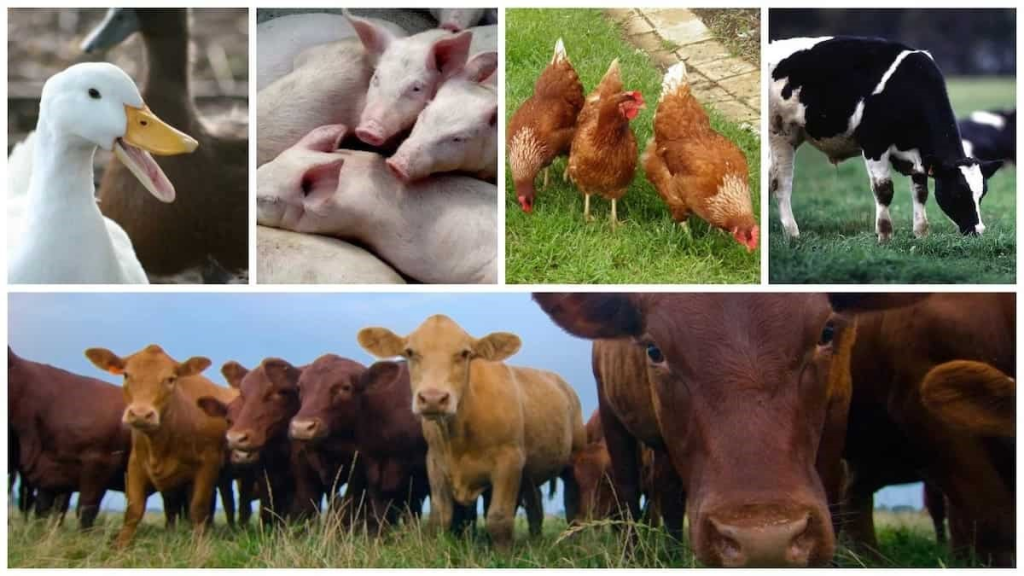

Livestock rearing involves raising animals such as cattle, poultry, pigs, or goats for various purposes including meat, milk, eggs, and fiber production. It contributes to diversified income streams for farmers, enhancing economic resilience. Livestock play a vital role in integrated farming systems by providing valuable manure for fertilizing crops and by grazing on pasture lands, which helps manage vegetation and reduce fire hazards. Proper management of livestock ensures efficient nutrient cycling and enhances soil fertility. Additionally, livestock rearing promotes food security by providing a sustainable source of animal protein for human consumption.
Agroforestry
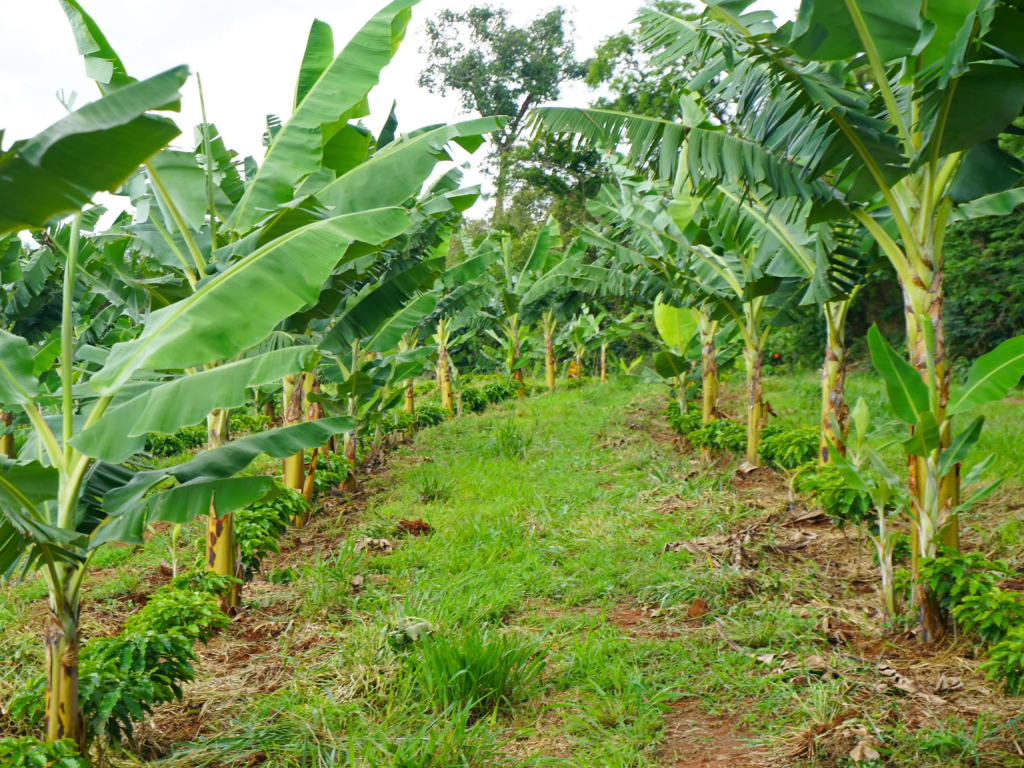

Agroforestry integrates trees or shrubs into agricultural systems, offering multiple benefits such as improved soil fertility, enhanced biodiversity, and increased resilience to climate change. It combines agricultural crops with tree crops or forest patches, optimizing land use and providing additional sources of income from timber, fruits, nuts, or medicinal plants. Agroforestry practices help mitigate environmental degradation by preventing soil erosion, conserving water, and sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This approach promotes sustainable land management and supports rural livelihoods by diversifying farm products and creating additional revenue streams. Overall, agroforestry contributes to more resilient and productive farming systems while preserving and restoring ecosystem health.
Aquaculture
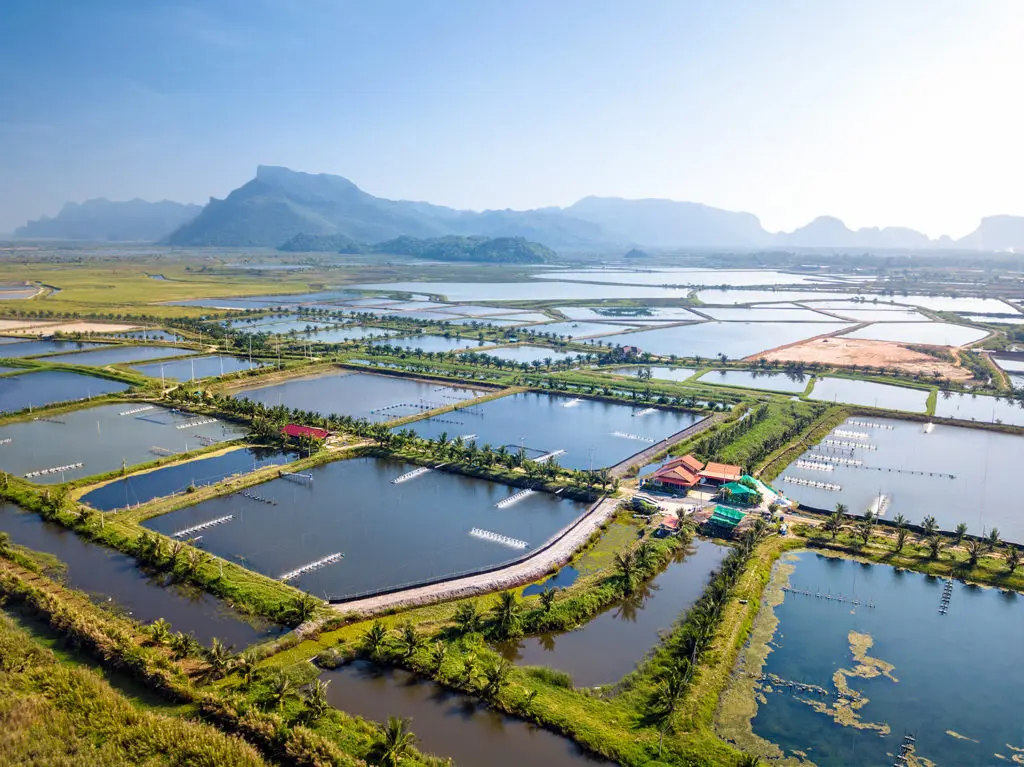

Aquaculture involves the farming of aquatic organisms such as fish, shellfish, and aquatic plants in controlled environments like ponds, tanks, or ocean pens. It provides a sustainable source of protein for human consumption, reducing pressure on wild fish populations. Aquaculture contributes to food security, economic growth, and rural development by generating employment opportunities in coastal and inland communities. By adopting responsible practices, aquaculture can minimize environmental impacts and promote conservation of aquatic ecosystems. Research and innovation in aquaculture technologies continue to enhance production efficiency, product quality, and environmental sustainability in this rapidly growing industry.
Vermicomposting

Vermicompost is a nutrient-rich organic fertilizer produced through the decomposition of organic materials by earthworms. It enhances soil fertility, improves soil structure, and promotes healthy plant growth. Vermicomposting is an eco-friendly practice that reduces the volume of organic waste and prevents it from ending up in landfills, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The process of vermicomposting also generates valuable by-products such as worm castings, which further enrich soil health. By utilizing vermicompost, farmers can reduce their dependency on synthetic fertilizers and contribute to sustainable agriculture.
Beekeeping

Beekeeping involves the management of bee colonies for honey production, pollination services, and other bee-derived products like beeswax and royal jelly. It plays a crucial role in agricultural ecosystems by enhancing crop yields through pollination, benefiting both farmers and the environment. Beekeeping promotes biodiversity by supporting the health of bee populations, which are essential pollinators for a wide variety of crops and wild plants. It provides opportunities for rural livelihoods and income diversification, particularly in areas with suitable floral resources for bees. Sustainable beekeeping practices prioritize the health and welfare of bee colonies while ensuring the conservation of bee habitats and forage sources.
Integrated Pest Management
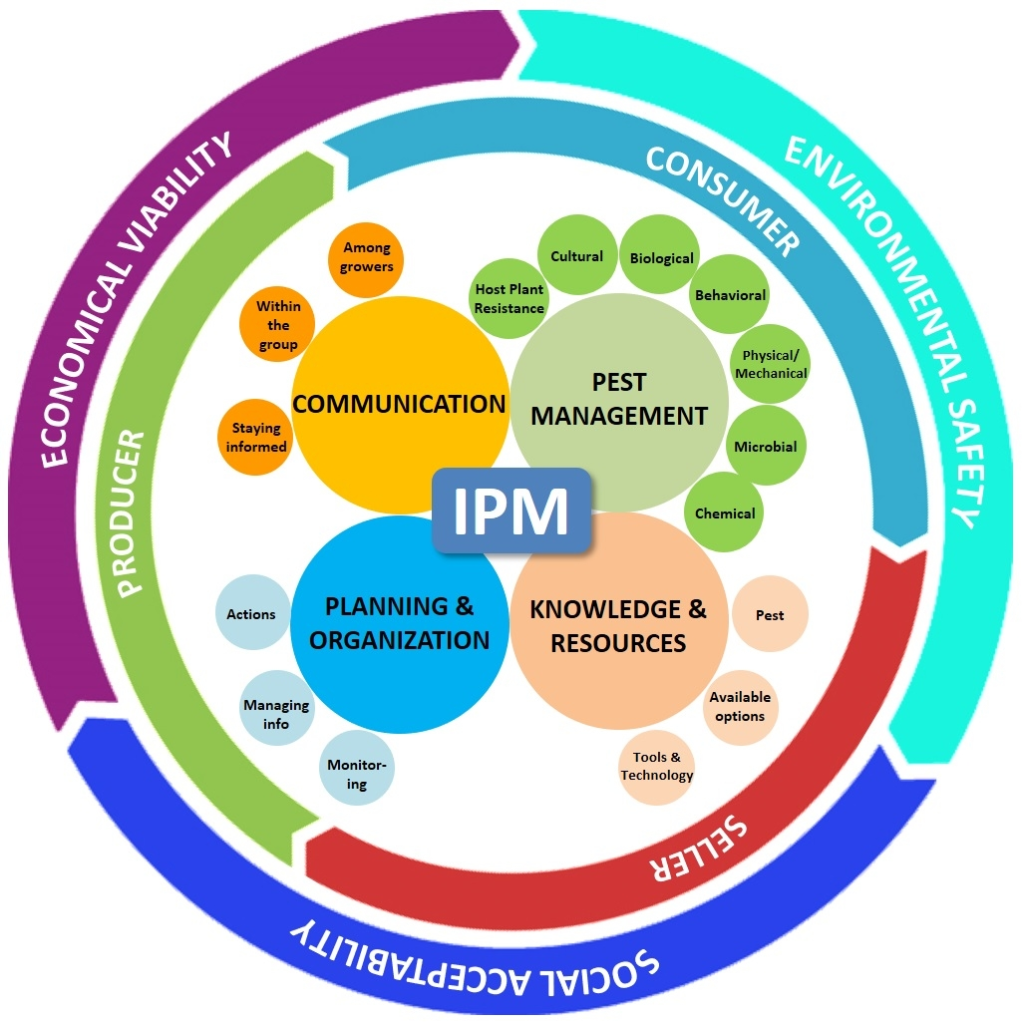
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic approach to pest control that emphasizes prevention, monitoring, and intervention strategies to minimize damage to crops while minimizing environmental impact. IPM integrates multiple control tactics, such as cultural practices, biological control agents, and selective pesticide use, to manage pests effectively. By using a combination of methods, IPM reduces reliance on chemical pesticides, mitigates the development of pest resistance, and preserves beneficial insect populations. It promotes sustainable agriculture by maintaining ecological balance and reducing risks to human health and the environment associated with pesticide exposure. Effective implementation of IPM requires continuous monitoring, knowledge of pest biology, and adaptation to changing pest pressures and environmental conditions.
Farm Waste Recycling

Farm waste recycling involves the conversion of agricultural by-products and residues into valuable resources such as compost, biochar, and biogas. This process reduces waste accumulation on farms while providing organic fertilizers and renewable energy sources. Recycling farm waste contributes to soil health and fertility by returning essential nutrients and organic matter to the soil. It mitigates environmental pollution by preventing the release of greenhouse gases and contaminants associated with decomposing organic waste. Implementing farm waste recycling practices supports sustainable agriculture, enhances resource efficiency, and fosters circular economy principles within farming systems.
Papaya Plantation

Papaya plantation offers a lucrative opportunity for agricultural ventures due to its fast growth and high yield potential. With proper care and maintenance, papaya trees can bear fruit within a year of planting, providing a relatively quick return on investment. Their adaptability to various soil types and climates makes them suitable for cultivation in diverse regions. Papaya plants are known for their resilience against pests and diseases, requiring minimal chemical intervention for successful growth. Additionally, papayas are rich in vitamins and antioxidants, contributing to their popularity in both local and international markets.
Soil Health Improvement

Soil health improvement is crucial for sustaining agriculture and ecosystem resilience. It involves enhancing soil fertility, structure, and biological activity to support plant growth and ecosystem functions. Implementing practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and organic amendments can improve soil health by replenishing nutrients and fostering microbial diversity. Healthy soils help sequester carbon, mitigate erosion, and retain water, contributing to climate change mitigation and water conservation efforts. Prioritizing soil health ensures sustainable land use and resilient agricultural systems, promoting food security and environmental sustainability.
